ICGOO在线商城 > 集成电路(IC) > PMIC - 稳流/电流管理 > INA138NA/250
- 型号: INA138NA/250
- 制造商: Texas Instruments
- 库位|库存: xxxx|xxxx
- 要求:
| 数量阶梯 | 香港交货 | 国内含税 |
| +xxxx | $xxxx | ¥xxxx |
查看当月历史价格
查看今年历史价格
INA138NA/250产品简介:
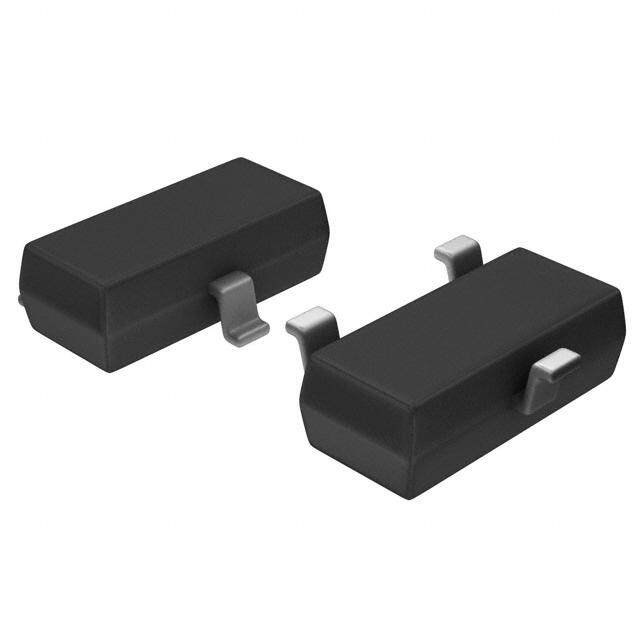
ICGOO电子元器件商城为您提供INA138NA/250由Texas Instruments设计生产,在icgoo商城现货销售,并且可以通过原厂、代理商等渠道进行代购。 INA138NA/250价格参考。Texas InstrumentsINA138NA/250封装/规格:PMIC - 稳流/电流管理, Current Monitor Regulator High-Side SOT-23-5。您可以下载INA138NA/250参考资料、Datasheet数据手册功能说明书,资料中有INA138NA/250 详细功能的应用电路图电压和使用方法及教程。
Texas Instruments(德州仪器)的INA138NA/250是一款属于PMIC - 稳流/电流管理类别的高精度双向零漂移仪表放大器,主要用于电流检测应用。其典型应用场景包括电源管理系统、电池供电设备、工业控制系统和电机控制等。 该器件通过检测串联在电路中的小阻值采样电阻两端的电压差,精确放大并输出与负载电流成比例的信号,支持低至2.7V、高达36V的宽工作电压范围,适合多种电源环境。INA138NA/250具备高共模抑制比(CMRR)和低温漂特性,能够在存在较大共模电压干扰的环境中稳定工作,确保测量精度。 常见应用包括:笔记本电脑、便携式电子设备中的电池充放电电流监测;服务器和通信设备中的电源监控;工业PLC模块中的实时电流反馈;以及电动汽车和储能系统中的电流传感环节。此外,因其采用小型化SOT-23-6封装,适用于空间受限的高密度电路板设计。 总之,INA138NA/250凭借其高精度、宽电压范围和优良稳定性,广泛用于需要可靠电流检测的各种中高端电子系统中。
| 参数 | 数值 |
| 产品目录 | 集成电路 (IC)半导体 |
| 描述 | IC CURRENT MONITOR 0.5% SOT23-5电流和电力监控器、调节器 Hi-Sd Msmnt Current Shunt Mntr Crnt Otp |
| 产品分类 | |
| 品牌 | Texas Instruments |
| 产品手册 | |
| 产品图片 |
|
| rohs | 符合RoHS无铅 / 符合限制有害物质指令(RoHS)规范要求 |
| 产品系列 | 电源管理 IC,电流和电力监控器、调节器,Texas Instruments INA138NA/250- |
| 数据手册 | |
| 产品型号 | INA138NA/250 |
| PCN其它 | |
| 产品 | Current Monitors |
| 产品培训模块 | http://www.digikey.cn/PTM/IndividualPTM.page?site=cn&lang=zhs&ptm=12392 |
| 产品目录页面 | |
| 产品种类 | 电流和电力监控器、调节器 |
| 供应商器件封装 | SOT-23-5 |
| 其它名称 | INA138NACT |
| 准确性 | +/- 0.5 % |
| 制造商产品页 | http://www.ti.com/general/docs/suppproductinfo.tsp?distId=10&orderablePartNumber=INA138NA/250 |
| 功能 | 电流监控器 |
| 包装 | 剪切带 (CT) |
| 单位重量 | 17.500 mg |
| 商标 | Texas Instruments |
| 安装类型 | 表面贴装 |
| 安装风格 | SMD/SMT |
| 封装 | Reel |
| 封装/外壳 | SC-74A,SOT-753 |
| 封装/箱体 | SOT-23-5 |
| 工作温度 | -40°C ~ 125°C |
| 工作温度范围 | - 40 C to + 125 C |
| 工厂包装数量 | 250 |
| 感应方式 | High Side |
| 感应方法 | 高端 |
| 标准包装 | 1 |
| 电压-输入 | 2.7 V ~ 36 V |
| 电流-输出 | - |
| 电源电压-最大 | 36 V |
| 电源电压-最小 | 2.7 V |
| 电源电流 | 0.045 mA |
| 精度 | ±0.5% |
| 系列 | INA138 |
| 输入电压范围 | 2.7 V to 36 V |








- 商务部:美国ITC正式对集成电路等产品启动337调查
- 曝三星4nm工艺存在良率问题 高通将骁龙8 Gen1或转产台积电
- 太阳诱电将投资9.5亿元在常州建新厂生产MLCC 预计2023年完工
- 英特尔发布欧洲新工厂建设计划 深化IDM 2.0 战略
- 台积电先进制程称霸业界 有大客户加持明年业绩稳了
- 达到5530亿美元!SIA预计今年全球半导体销售额将创下新高
- 英特尔拟将自动驾驶子公司Mobileye上市 估值或超500亿美元
- 三星加码芯片和SET,合并消费电子和移动部门,撤换高东真等 CEO
- 三星电子宣布重大人事变动 还合并消费电子和移动部门
- 海关总署:前11个月进口集成电路产品价值2.52万亿元 增长14.8%





PDF Datasheet 数据手册内容提取
Product Order Technical Tools & Support & Reference Folder Now Documents Software Community Design INA138,INA168 SBOS122E–DECEMBER1999–REVISEDDECEMBER2017 INA1x8 High-Side Measurement Current Shunt Monitor 1 Features 3 Description • CompleteUnipolarHigh-SideCurrent The INA138 and INA168 (INA1x8) are high-side, 1 unipolar, current shunt monitors. Wide input common- MeasurementCircuit mode voltage range, low quiescent current, and tiny • WideSupplyandCommon-ModeRange SOT-23 packaging enable use in a variety of • INA138:2.7Vto36V applications. • INA168:2.7Vto60V Input common-mode and power-supply voltages are • IndependentSupplyandInputCommon-Mode independent and can range from 2.7 V to 36 V for the Voltages INA138 and 2.7 V to 60 V for the INA168. Quiescent current is only 25 µA, which permits connecting the • SingleResistorGainSet power supply to either side of the current • LowQuiescentCurrent(25µATypical) measurementshuntwithminimalerror. • WideTemperatureRange:–40°Cto+125°C The device converts a differential input voltage to a • 5-PinSOT-23Package current output. This current is converted back to a voltage with an external load resistor that sets any 2 Applications gain from 1 to over 100. Although designed for current shunt measurement, the circuit invites • CurrentShuntMeasurement: creative applications in measurement and level – Telephone,Computers shifting. • PortableandBattery-BackupSystems Both the INA138 and INA168 are available in SOT23- • BatteryChargers 5 and are specified for the –40°C to 125°C • PowerManagement temperaturerange. • CellPhones DeviceInformation(1) • PrecisionCurrentSource PARTNUMBER PACKAGE BODYSIZE(NOM) INA138 SOT-23(5) 2.90mm×1.60mm INA168 (1) Forallavailablepackages,seethepackageoptionaddendum attheendofthedatasheet. TypicalApplicationCircuit RS IS V IN+ UpTo60 V 3 4 V V IN+ IN– Load 5 kΩ 5 kΩ V+ 5 OUT V =I R R /5 kΩ GND 1 O S S L 2 Copyright © 1999,Texas Instruments Incorporated 1 An IMPORTANT NOTICE at the end of this data sheet addresses availability, warranty, changes, use in safety-critical applications, intellectualpropertymattersandotherimportantdisclaimers.PRODUCTIONDATA.
INA138,INA168 SBOS122E–DECEMBER1999–REVISEDDECEMBER2017 www.ti.com Table of Contents 1 Features.................................................................. 1 8 ApplicationandImplementation........................ 10 2 Applications........................................................... 1 8.1 ApplicationInformation............................................10 3 Description............................................................. 1 8.2 TypicalApplications ...............................................11 4 RevisionHistory..................................................... 2 9 PowerSupplyRecommendations...................... 18 5 PinConfigurationandFunctions......................... 3 10 Layout................................................................... 18 6 Specifications......................................................... 4 10.1 LayoutGuidelines.................................................18 6.1 AbsoluteMaximumRatings......................................4 10.2 LayoutExample....................................................18 6.2 ESDRatings ............................................................4 11 DeviceandDocumentationSupport................. 19 6.3 RecommendedOperatingConditions.......................4 11.1 DocumentationSupport .......................................19 6.4 ThermalInformation .................................................5 11.2 RelatedLinks........................................................19 6.5 ElectricalCharacteristics...........................................5 11.3 ReceivingNotificationofDocumentationUpdates19 6.6 TypicalCharacteristics..............................................6 11.4 CommunityResources..........................................19 7 DetailedDescription.............................................. 8 11.5 Trademarks...........................................................19 7.1 Overview...................................................................8 11.6 ElectrostaticDischargeCaution............................19 7.2 FunctionalBlockDiagram.........................................8 11.7 Glossary................................................................19 7.3 FeatureDescription...................................................9 12 Mechanical,Packaging,andOrderable Information........................................................... 20 7.4 DeviceFunctionalModes..........................................9 4 Revision History NOTE:Pagenumbersforpreviousrevisionsmaydifferfrompagenumbersinthecurrentversion. ChangesfromRevisionD(December2014)toRevisionE Page • Addedreferencedesignlinktonavigationbaratthetopofthefrontpage........................................................................... 1 • Changedbodysizefrom18.00mm×18.00mmto2.90mm×1.60mminDeviceInformationtable.................................. 1 • Changedpinnumbersinpinfunctionstabletomatchpinconfigurationfigure...................................................................... 3 • ChangedAbsoluteMaximumRatingstableforclarity;novalueswerechanged ................................................................. 4 • ChangedRecommendedOperatingConditionstable;movedsomecontentfromElectricalCharacteristicstable,but novalueschanged................................................................................................................................................................. 4 • ChangedallvaluesinThermalInformationtable................................................................................................................... 5 • ChangedElectricalCharacteristicstable;reformattedforclarity;movedsomecontenttoRecommendedOperating Conditionstable,anddeletedduplicatecontent..................................................................................................................... 5 • Changedcommon-moderejectiontestconditionstobetterhighlighteachdeviceinElectricalCharacteristicstable ..........5 • ChangedoffsetvoltagevstemperaturetooffsetvoltagedriftinElectricalCharacteristicstable........................................... 5 • ChangedoffsetvoltagevspowersupplytestconditionstobetterhighlighteachdeviceinElectricalCharacteristicstable.5 • ChangedreferenceintextfromFigure10toFigure11inlastparagraphofSelectingtheShuntResistorandR section 12 L ChangesfromRevisionC(November2005)toRevisionD Page • AddedESDRatingstable,FeatureDescriptionsection,DeviceFunctionalModes,ApplicationandImplementation section,PowerSupplyRecommendationssection,Layoutsection,DeviceandDocumentationSupportsection,and Mechanical,Packaging,andOrderableInformationsection. ................................................................................................ 1 2 SubmitDocumentationFeedback Copyright©1999–2017,TexasInstrumentsIncorporated ProductFolderLinks:INA138 INA168
INA138,INA168 www.ti.com SBOS122E–DECEMBER1999–REVISEDDECEMBER2017 5 Pin Configuration and Functions DBVPackage 5-PinSOT-23 TopView OUT 1 5 V+ GND 2 VIN+ 3 4 VIN– Not to scale PinFunctions PIN I/O DESCRIPTION NO. NAME 1 OUT O Outputcurrent 2 GND — Ground 3 VIN+ I Positiveinputvoltage 4 VIN– I Negativeinputvoltage 5 V+ I Powersupplyvoltage Copyright©1999–2017,TexasInstrumentsIncorporated SubmitDocumentationFeedback 3 ProductFolderLinks:INA138 INA168
INA138,INA168 SBOS122E–DECEMBER1999–REVISEDDECEMBER2017 www.ti.com 6 Specifications 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings overoperatingfree-airtemperaturerange(unlessotherwisenoted) (1) MIN MAX UNIT INA138 –0.3 60 Supply,V+ INA168 –0.3 75 Commonmode(2) –0.3 60 INA138 Voltage Sensevoltage,V =(V –V ) –40 2 V SENSE IN+ IN– Analoginput,V ,V IN+ IN– Commonmode(2) –0.3 75 INA168 Sensevoltage,V =(V –V ) –40 2 SENSE IN+ IN– Analogoutput,OUTpin(2) –0.3 40 Current Inputcurrentintoanypin 10 mA Operating,T –55 150 A Temperature Junction,T 150 °C J Storage,T –65 150 stg (1) StressesbeyondthoselistedunderAbsoluteMaximumRatingsmaycausepermanentdamagetothedevice.Thesearestressratings only,whichdonotimplyfunctionaloperationofthedeviceattheseoranyotherconditionsbeyondthoseindicatedunderRecommended OperatingConditions.Exposuretoabsolute-maximum-ratedconditionsforextendedperiodsmayaffectdevicereliability. (2) Theinputvoltageatanypinmayexceedthevoltageshownifthecurrentatthatpinislimitedto10mA. 6.2 ESD Ratings VALUE UNIT Human-bodymodel(HBM),perANSI/ESDA/JEDECJS-001(1) ±1000 V Electrostaticdischarge V (ESD) Charged-devicemodel(CDM),perJEDECspecificationJESD22-C101(2) ±500 (1) JEDECdocumentJEP155statesthat500-VHBMallowssafemanufacturingwithastandardESDcontrolprocess. (2) JEDECdocumentJEP157statesthat250-VCDMallowssafemanufacturingwithastandardESDcontrolprocess. 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions overoperatingfree-airtemperaturerange(unlessotherwisenoted) MIN NOM MAX UNIT INA138 V+ Supplyvoltage 2.7 5 36 V V Full-scalesensevoltage(V –V ) 100 500 mV SENSE IN+ IN– Common-modevoltage 2.7 12 36 V T Operatingtemperature –40 25 125 °C A INA168 V+ Supplyvoltage 2.7 5 60 V V Full-scalesensevoltage(V –V ) 100 500 mV SENSE IN+ IN– Common-modevoltage 2.7 12 60 V T Operatingtemperature –40 25 125 °C A 4 SubmitDocumentationFeedback Copyright©1999–2017,TexasInstrumentsIncorporated ProductFolderLinks:INA138 INA168
INA138,INA168 www.ti.com SBOS122E–DECEMBER1999–REVISEDDECEMBER2017 6.4 Thermal Information INA1x8 THERMALMETRIC(1) DBV UNIT 5PINS R Junction-to-ambientthermalresistance 168.3 °C/W θJA R Junction-to-case(top)thermalresistance 73.8 °C/W θJC(top) R Junction-to-boardthermalresistance 28.1 °C/W θJB ψ Junction-to-topcharacterizationparameter 2.5 °C/W JT ψ Junction-to-boardcharacterizationparameter 27.6 °C/W JB (1) Formoreinformationabouttraditionalandnewthermalmetrics,seetheSemiconductorandICPackageThermalMetricsapplication report. 6.5 Electrical Characteristics allothercharacteristicsatT =+25°C,V =5V,V =12V,andR =125kΩ(unlessotherwisenoted) A S IN+ OUT INA1x8 PARAMETER TESTCONDITIONS UNIT MIN TYP MAX INPUT INA138,VIN+=2.7Vto36V 100 120 Common-moderejection VSENSE=50mV dB INA168,VIN+=2.7Vto60V 100 120 Offsetvoltage(1) TA=25°C ±0.2 ±1 mV TA=–40°Cto+125°C ±2 Offsetvoltagedrift(1) TA=–40°Cto+125°C 1 µV/°C INA138,V+=2.7Vto36V 0.1 10 Offsetvoltagevspowersupply,V+ VSENSE=50mV µV/V INA168,V+=2.7Vto60V 0.1 10 TA=25°C 2 Inputbiascurrent µA TA=–40°Cto+125°C,INA138 10 OUTPUT VSENSE=10mVto150mV,TA=25°C 198 200 202 µA/V Transconductance VSENSE=100mV,TA=–40°Cto+125°C 196 204 µA/V Transconductancedrift TA=–40°Cto+125°C 10 nA/°C Nonlinearityerror VSENSE=10mVto150mV ±0.01% ±0.1% TA=25°C ±0.5% ±2% Totaloutputerror VSENSE=100mV TA=–40°Cto+125°C ±2.5% Outputimpedance 1||5 GΩ||pF Topowersupplyvoltage,V+ (V+)–0.8 (V+)–1.0 V Voltageoutputswing Tocommon-modevoltage,VCM VCM–0.5 VCM–0.8 V FREQUENCYRESPONSE ROUT=5kΩ 800 kHz Bandwidth ROUT=125kΩ 32 kHz 5-Vstep,ROUT=5kΩ 1.8 µs Settlingtime To0.1% 5-Vstep,ROUT=125kΩ 30 µs NOISE Output-currentnoisedensity 9 pA/√Hz Totaloutput-currentnoise BW=100kHz 3 nARMS POWERSUPPLY Quiescentcurrent VSENSE=0V, TA=25°C 25 45 µA IO=0mA TA=–40°Cto+125°C 60 µA (1) Definedastheamountofinputvoltage,V ,todrivetheoutputtozero. SENSE Copyright©1999–2017,TexasInstrumentsIncorporated SubmitDocumentationFeedback 5 ProductFolderLinks:INA138 INA168
INA138,INA168 SBOS122E–DECEMBER1999–REVISEDDECEMBER2017 www.ti.com 6.6 Typical Characteristics AtT =+25°C,V+=5V,V =12V,andR =125kΩ,unlessotherwisenoted. A IN+ L 40 120 R =500kΩ L G=100 30 B) 100 d R =50kΩ ( L n dB) 20 ejectio 80 G =10 ( 10 R Gain 0 RL=5kΩ Mode 60 G = 1 -n 40 o m –10 m CL=10nF CL=1nF CL=100pF Co 20 –20 100 1k 10k 100k 1M 10M 0 0.1 1 10 100 1k 10k 100k Frequency(Hz) Frequency(Hz) Figure1.GainvsFrequency Figure2.Common-ModeRejectionvsFrequency 140 5 –55°C VIN=(VIN+ –VIN–) B) 120 (dn G=100 %) 0 o 100 ( Rejecti 80 G = 10 Erutror –5 +150°C pply G = 1 Outp +25°C Su 60 al er- Tot –10 w Po 40 –15 20 0 25 50 75 100 125 150 200 1 10 100 1k 10k 100k V (mV) Frequency(Hz) IN Figure4.TotalOutputErrorvsV Figure3.Power-SupplyRejectionvsFrequency IN 2 50 Outputerrorisessentially independentofboth +150° 40 utError(%) 10 Vin+pustucpopmlymvoolnta-mgeodaendvoltage. G = 1 µC(Aurrent) 30 ++12255°° otalOutp –1 G =25 G =10 uiescent 20 Use(VI+N–)A5>156°386Vwith T Q 10 –2 0 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 Power-SupplyVoltage(V) Power-SupplyVoltage(V) Figure5.TotalOutputErrorvsPower-SupplyVoltage Figure6.QuiescentCurrentvsPower-SupplyVoltage 6 SubmitDocumentationFeedback Copyright©1999–2017,TexasInstrumentsIncorporated ProductFolderLinks:INA138 INA168
INA138,INA168 www.ti.com SBOS122E–DECEMBER1999–REVISEDDECEMBER2017 Typical Characteristics (continued) AtT =+25°C,V+=5V,V =12V,andR =125kΩ,unlessotherwisenoted. A IN+ L m m Figure7.StepResponse Figure8.StepResponse Copyright©1999–2017,TexasInstrumentsIncorporated SubmitDocumentationFeedback 7 ProductFolderLinks:INA138 INA168
INA138,INA168 SBOS122E–DECEMBER1999–REVISEDDECEMBER2017 www.ti.com 7 Detailed Description 7.1 Overview The INA138 and INA168 devices (INA1x8) are comprised of a high voltage, precision operational amplifier, precision thin film resistors trimmed in production to an absolute tolerance and a low noise output transistor. The INA1x8 devices can be powered from a single power supply and their input voltages can exceed the power supply voltage. The INA1x8 devices are ideal for measuring small differential voltages, such as those generated across a shunt resistor, in the presence of large common-mode voltages. Refer to Functional Block Diagram whichillustratesthefunctionalcomponentswithinbothINA1x8devices. 7.2 Functional Block Diagram VIN+ VIN– V+ OUT GND Copyright © 2014,Texas Instruments Incorporated 8 SubmitDocumentationFeedback Copyright©1999–2017,TexasInstrumentsIncorporated ProductFolderLinks:INA138 INA168
INA138,INA168 www.ti.com SBOS122E–DECEMBER1999–REVISEDDECEMBER2017 7.3 Feature Description 7.3.1 OutputVoltageRange The output of the INA1x8 device is a current that is converted to a voltage by the load resistor, R . The output L current remains accurate within the compliance voltage range of the output circuitry. The shunt voltage and the input common-mode and power-supply voltages limit the maximum possible output swing. The maximum output voltage(V )complianceislimitedbyeitherEquation1orEquation2,whicheverislower: outmax V =(V+)–0.7V–(V –V ) (1) outmax IN+ IN– or V =V –0.5V (2) outmax IN– 7.3.2 Bandwidth Measurement bandwidth is affected by the value of the load resistor, R . High gain produced by high values of L R will yield a narrower measurement bandwidth (see Typical Characteristics). For widest possible bandwidth, L keep the capacitive load on the output to a minimum. Reduction in bandwidth due to capacitive load is shown in theTypicalCharacteristics. If bandwidth limiting (filtering) is desired, a capacitor can be added to the output (see Figure 12). This will not causeinstability. 7.4 Device Functional Modes For proper operation the INA1x8 devices must operate within their specified limits. Operating either device outside of their specified power supply voltage range or their specified common-mode range will result in unexpectedbehaviorandisnotrecommended.Additionallyoperatingtheoutputbeyondtheirspecifiedlimitswith respect to power supply voltage and input common-mode voltage will also produce unexpected results. Refer to ElectricalCharacteristicsforthedevicespecifications. Copyright©1999–2017,TexasInstrumentsIncorporated SubmitDocumentationFeedback 9 ProductFolderLinks:INA138 INA168
INA138,INA168 SBOS122E–DECEMBER1999–REVISEDDECEMBER2017 www.ti.com 8 Application and Implementation NOTE Information in the following applications sections is not part of the TI component specification, and TI does not warrant its accuracy or completeness. TI’s customers are responsible for determining suitability of components for their purposes. Customers should validateandtesttheirdesignimplementationtoconfirmsystemfunctionality. 8.1 Application Information 8.1.1 Operation Figure 9 illustrates the basic circuit diagram for both the INA138 and INA168 devices. Load current I is drawn S from supply V through shunt resistor R . The voltage drop in shunt resistor V is forced across R by the S S S G1 internal op amp, causing current to flow into the collector of Q1. External resistor R converts the output current L toavoltage,V ,attheOUTpin.ThetransferfunctionfortheINA138deviceis: OUT I =g (V –V ) (3) O m IN+ IN– whereg =200µA/V. m In the circuit of Figure 9, the input voltage, (V – V ), is equal to I × R and the output voltage, V , is equal IN+ IN– S S OUT to I × R . The transconductance, g , of the INA138 device is 200 µA/V. The complete transfer function for the O L m currentmeasurementamplifierinthisapplicationis: V =(I )(R )(200µA/V)(R ) (4) OUT S S L The maximum differential input voltage for accurate measurements is 0.5 V, which produces a 100-µA output current. A differential input voltage of up to 2 V will not cause damage. Differential measurements (pins 3 and 4) must be unipolar with a more-positive voltage applied to pin 3. If a more-negative voltage is applied to pin 3, the outputcurrent,I ,willbezero,butitwillnotcausedamage. O V P LoadPowerSupply 2.7 V to 36 V(1) Shunt R S I S V V IN+ IN– 3 4 V+powercanbecommonor V+ Load independentofloadsupply. RG1 RG2 5 kΩ 5 kΩ 2.7 V ≤ (V+) ≤ 36 V(1) 5 Q1 VOLTAGEGAIN EXACTR (Ω) NEAREST1%R (Ω) L L OUT INA138 1 5k 4.99k 1 + 2 I 2 10k 10k 0 R V 5 25k 24.9k L O 10 50k 49.9k – 20 100k 100k 50 250k 249k 100 500k 499k Copyright © 1999,Texas Instruments Incorporated (1) MaximumV andV+voltageis60VwithINA168. P Figure9. BasicCircuitConnections 10 SubmitDocumentationFeedback Copyright©1999–2017,TexasInstrumentsIncorporated ProductFolderLinks:INA138 INA168
INA138,INA168 www.ti.com SBOS122E–DECEMBER1999–REVISEDDECEMBER2017 8.2 Typical Applications The INA1x8 devices are designed for current shunt measurement circuits, as shown in Figure 9, but basic device functionisusefulinawiderangeofcircuitry.Acreativeengineerwillfindmanyunforeseenusesinmeasurement andlevel-shiftingcircuits.AfewideasareillustratedinFigure10throughFigure18. 8.2.1 BufferingOutputtoDriveanADC IS VIN+ VIN- OPA340 INA138 + RS or ADC INA168 Buffer amplifier C RL drives ADC without affecting gain Figure10. BufferingOutputtoDriveanADC 8.2.1.1 DesignRequirements DigitizetheoutputoftheINA1x8devicesusinga1-MSPSanalog-to-digitalconverter(ADC). 8.2.1.2 DetailedDesignProcedure 8.2.1.2.1 SelectingtheShuntResistorandR L In Figure 9 the value chosen for the shunt resistor depends on the application and is a compromise between small-signal accuracy and maximum permissible voltage loss in the measurement line. High values of shunt resistor provide better accuracy at lower currents by minimizing the effects of offset, while low values of shunt resistor minimize voltage loss in the supply line. For most applications, best performance is attained with a shunt resistor value that provides a full-scale shunt voltage range of 50 mV to 100 mV. Maximum input voltage for accuratemeasurementsis500mV. The load resistor, R , is chosen to provide the desired full-scale output voltage. The output impedance of the L INA1x8 OUT terminal is very high which permits using values of R up to 500 kΩ with excellent accuracy. The L input impedance of any additional circuitry at the output should be much higher than the value of R to avoid L degradingaccuracy. Someanalog-to-digitalconverters(ADCs)haveinputimpedancesthatsignificantlyaffectmeasurementgain.The input impedance of the ADC can be included as part of the effective R if its input can be modeled as a resistor L to ground. Alternatively, an op amp can be used to buffer the ADC input. The INA1x8 are current output devices, and as such have an inherently large output impedance. The output currents from the amplifier are converted to an output voltage via the load resistor, R , connected from the amplifier output to ground. The ratio of the load L resistorvaluetothatoftheinternalresistorvaluedeterminesthevoltagegainofthesystem. In many applications digitizing the output of the INA1x8 device is required, and can be accomplished by connecting the output of the amplifier to an ADC. It is very common for an ADC to have a dynamic input impedance. If the INA1x8 output is connected directly to an ADC input, the input impedance of the ADC is effectively connected in parallel with the gain setting resistor R . This parallel impedance combination will affect L the gain of the system and the impact on the gain is difficult to estimate accurately. A simple solution that eliminates the paralleling of impedances, simplifying the gain of the circuit is to place a buffer amplifier, such as theOPA340,betweentheoutputoftheINA138orINA168deviceandtheinputtotheADC. Copyright©1999–2017,TexasInstrumentsIncorporated SubmitDocumentationFeedback 11 ProductFolderLinks:INA138 INA168
INA138,INA168 SBOS122E–DECEMBER1999–REVISEDDECEMBER2017 www.ti.com Typical Applications (continued) Figure10illustratesthisconcept.NoticethatalowpassfilterisplacedbetweentheOPA340outputandtheinput to the ADC. The filter capacitor is required to provide any instantaneous demand for current required by the input stage of the ADC. The filter resistor is required to isolate the OPA340 output from the filter capacitor to maintain circuit stability. The values for the filter components will vary according to the operational amplifier used for the buffer and the particular ADC selected. More information can be found regarding the design of the low pass filter in the TI Precision Design , 16 bit 1MSPS Data Acquisition Reference Design for Single-Ended Multiplexed Applications(TIPD173). Figure 11 shows the expected results when driving an analog-to-digital converter at 1MSPS with and without buffering the INA1x8 output. Without the buffer, the high impedance of the INA1x8 reacts with the input capacitance and sample and hold (S/H) capacitance of the ADC, and does not allow the S/H to reach the correct final value before it is reset and the next conversion starts. Adding the buffer amplifier significantly reduces the output impedance driving the S/H and allows for higher conversion rates than can be achieved without adding thebuffer. 8.2.1.3 ApplicationCurve with buffer without Buffer v) di V/ 5 2 0. C ( D A o ut t p n I Time Figure11. DrivinganADCWithandWithoutaBuffer 12 SubmitDocumentationFeedback Copyright©1999–2017,TexasInstrumentsIncorporated ProductFolderLinks:INA138 INA168
INA138,INA168 www.ti.com SBOS122E–DECEMBER1999–REVISEDDECEMBER2017 Typical Applications (continued) 8.2.2 OutputFilter 3 4 f –3dB 1 INA138 f = –3dB 2πRC L L V O RL CL Figure12. OutputFilter 8.2.2.1 DesignRequirements FiltertheoutputoftheINA1x8devices. 8.2.2.2 DetailedDesignProcedure A low-pass filter can be formed at the output of the INA1x8 devices simply by placing a capacitor of the desired value in parallel with the load resistor. First determine the value of the load resistor needed to achieve the desired gain. Refer to the table in Figure 9. Next, determine the capacitor value that will result in the desired cutoff frequency according to the equation shown in Figure 12. Figure 13 illustrates various combinations of gain settings(determinedbyR )andfiltercapacitors. L 8.2.2.3 ApplicationCurve 40 R =500kΩ L 30 R =50kΩ L 20 B) d ( 10 n ai G RL=5kΩ 0 –10 C =10nF C =1nF C =100pF L L L –20 100 1k 10k 100k 1M 10M Frequency(Hz) Figure13. GainvsFrequency Copyright©1999–2017,TexasInstrumentsIncorporated SubmitDocumentationFeedback 13 ProductFolderLinks:INA138 INA168
INA138,INA168 SBOS122E–DECEMBER1999–REVISEDDECEMBER2017 www.ti.com Typical Applications (continued) 8.2.3 OffsettingtheOutputVoltage For many applications using only a single power supply it may be required to level shift the output voltage away from ground when there is no load current flowing in the shunt resistor. Level shifting the output of the INA1x8 devices is easily accomplished by one of two simple methods shown in Figure 14. The method on the left hand side of Figure 14 illustrates a simple voltage divider method. This method is useful for applications that require the output of the INA1x8 devices to remain centered with respect to the power supply at zero load current through the shunt resistor. Using this method the gain is determine by the parallel combination of R and R 1 2 while the output offset is determined by the voltage divider ratio R and R . For applications that may require a 1 2 fixed value of output offset, independent of the power supply voltage, the current source method shown on the right-hand side of Figure 14 is recommended. With this method a REF200 constant current source is used to generate a constant output offset. Using his method the gain is determined by R and the offset is determined by L theproductofthevalueofthecurrentsourceandR . L V+ 3 4 VR 3 4 REF200 INA138 R1 INA138 100 µA VO VO 1 1 R2 RL Gain Set by R1 || R2 Gain Set by RL (VR)R2 Output Offset = (100 µA)(RL) Output Offset = R1 + R2 (independent of V+) a) Using resistor divider. b) Using current source. Figure14. OffsettingtheOutputVoltage 14 SubmitDocumentationFeedback Copyright©1999–2017,TexasInstrumentsIncorporated ProductFolderLinks:INA138 INA168
INA138,INA168 www.ti.com SBOS122E–DECEMBER1999–REVISEDDECEMBER2017 Typical Applications (continued) 8.2.4 BipolarCurrentMeasurement The INA1x8 devices can be configured as shown in Figure 15 in applications where measuring current bi- directionallyisrequired.TwoINAdevicesarerequiredconnectingtheirinputsacrosstheshuntresistorasshown in Figure 15. A comparator, such as the TLV3201, is used to detect the polarity of the load current. The magnitude of the load current is monitored across the resistor connected between ground and the connection labeled Output. In this example the 100-kΩ resistor results in a gain of 20 V/V. The 10-kΩ resistors connected in series with the INA1x8 output current are used to develop a voltage across the comparator inputs. Two diodes are required to prevent current flow into the INA1x8 output, as only one device at a time is providing current to the Output connectionofthecircuit.ThecircuitfunctionalityisillustratedinFigure16. ±1 A Load Curent RSH 100 m(cid:13) VIN+ VIN– VIN– VIN+ Bus Load Voltage Current 5 k(cid:13)(cid:3) 5 k(cid:13)(cid:3) 5 k(cid:13)(cid:3) 5 k(cid:13)(cid:3) +5 V V+ V+ +5 V + + INA138 INA138 or OUT OUT or INA168 GND GND INA168 1N4148 1N4148 + Sign TLV3201 10 k(cid:13)(cid:3) 10 k(cid:13)(cid:3) Output 100 k(cid:13)(cid:3) Figure15. BipolarCurrentMeasurement Copyright©1999–2017,TexasInstrumentsIncorporated SubmitDocumentationFeedback 15 ProductFolderLinks:INA138 INA168
INA138,INA168 SBOS122E–DECEMBER1999–REVISEDDECEMBER2017 www.ti.com Typical Applications (continued) Load Current Output Sign e g a olt V Time Figure16. BipolarCurrentMeasurementsResults(arbitraryscale) 8.2.5 BipolarCurrentMeasurementUsingDifferentialInputofADC The INA1x8 devices can be used with an ADC such as the ADS7870 programmed for differential mode operation. Figure 17 illustrates this configuration. In this configuration the use of two INAs allows for bidirectional current measurement. Depending upon the polarity of the current, one of the INAs provides an output voltage, while the other output is zero. In this way the ADC reads the polarity of current directly, without the need for additionalcircuitry. R V+ S 4 3 3 4 +5V +5V +5V REF BUF BUF OUT IN OUT 5 5 REF BUF Digital I/O INA138 INA138 12-BitA/D 1 2 2 1 MUX PGIA Converter RL 25kΩ RL 25kΩ Clock Serial Divider ADS7870 I/O A/Dconverterprogrammedfordifferentialinput. Oscillator Dependingonpolarityofcurrent,oneINA138provides anoutputvoltage,theoutputoftheotheriszero. Figure17. BipolarCurrentMeasurementUsingDifferentialInputofADC 16 SubmitDocumentationFeedback Copyright©1999–2017,TexasInstrumentsIncorporated ProductFolderLinks:INA138 INA168
INA138,INA168 www.ti.com SBOS122E–DECEMBER1999–REVISEDDECEMBER2017 Typical Applications (continued) 8.2.6 MultiplexedMeasurementUsingLogicSignalforPower Multiple loads can be measured as illustrated in Figure 18. In this configuration each INA1x8 device is powered bythedigitalI/OfromtheADS7870.MultiplexingisachievedbyswitchingonoroffeachthedesiredI/O. OtherINA168s DigitalI/OontheADS7870providespowertoselect thedesiredINA168.Diodespreventoutputcurrentof theonINA168fromflowingintotheoffINA168. INA168 V+ +5V –– REF BUF BUF OUT IN OUT REF BUF Digital I/O INA168 V+ –– 12-BitA/D MUX PGIA Converter IN4148 Clock Serial Divider RL Oscillator ADS7870 I/O Figure18. MultiplexedMeasurementUsingLogicSignalforPower Copyright©1999–2017,TexasInstrumentsIncorporated SubmitDocumentationFeedback 17 ProductFolderLinks:INA138 INA168
INA138,INA168 SBOS122E–DECEMBER1999–REVISEDDECEMBER2017 www.ti.com 9 Power Supply Recommendations The input circuitry of the INA138 can accurately measure beyond its power-supply voltage, V+. For example, the V+ power supply can be 5 V, whereas the load power supply voltage is up to 36 V (or 60 V with the INA168). The output voltage range of the OUT terminal, however, is limited by the lesser of the two voltages (see Output Voltage Range). A 0.1-µF capacitor is recommenced to be placed near the power supply pin on the INA138 or INA168.Additionalcapacitancemayberequiredforapplicationswithnoisypowersupplyvoltages. 10 Layout 10.1 Layout Guidelines Figure 19 shows the basic connection of the INA138 device. The input pins, V and V , should be connected IN+ IN– as closely as possible to the shunt resistor to minimize any resistance in series with the shunt resistance. The output resistor, R , is shown connected between pin 1 and ground. Best accuracy is achieved with the output L voltage measured directly across R . This is especially important in high-current systems where load current L couldflowinthegroundconnections,affectingthemeasurementaccuracy. No power-supply bypass capacitors are required for stability of the INA138. However, applications with noisy or high-impedancepowersuppliesmayrequiredecouplingcapacitorstorejectpower-supplynoise.Connectbypass capacitorsclosetothedevicepins. 10.2 Layout Example VIA to Ground Plane INA138 INA168 Output OUT V+ Supply Voltage 0.1 µF GND RL VIN+ VIN- To Bus PCB pad PCB pad To Load Voltage RSHUNT Figure19. TypicalLayoutExample 18 SubmitDocumentationFeedback Copyright©1999–2017,TexasInstrumentsIncorporated ProductFolderLinks:INA138 INA168
INA138,INA168 www.ti.com SBOS122E–DECEMBER1999–REVISEDDECEMBER2017 11 Device and Documentation Support 11.1 Documentation Support 11.1.1 RelatedDocumentation Forrelateddocumentationseethefollowing: • 16bit1MSPSDataAcquisitionReferenceDesignforSingle-EndedMultiplexedApplications • ADS787012-BitADC,MUX,PGAandInternalReferenceDataAcquisitionSystem • TLV3201,TLV320240-ns,microPOWER,Push-PullOutputComparators • REF200DualCurrentSource/CurrentSink 11.2 Related Links Table 1 lists quick access links. Categories include technical documents, support and community resources, toolsandsoftware,andquickaccesstosampleorbuy. Table1.RelatedLinks TECHNICAL TOOLS& SUPPORT& PARTS PRODUCTFOLDER SAMPLE&BUY DOCUMENTS SOFTWARE COMMUNITY INA138 Clickhere Clickhere Clickhere Clickhere Clickhere INA168 Clickhere Clickhere Clickhere Clickhere Clickhere 11.3 Receiving Notification of Documentation Updates To receive notification of documentation updates, navigate to the device product folder on ti.com. In the upper right corner, click on Alert me to register and receive a weekly digest of any product information that has changed.Forchangedetails,reviewtherevisionhistoryincludedinanyreviseddocument. 11.4 Community Resources The following links connect to TI community resources. Linked contents are provided "AS IS" by the respective contributors. They do not constitute TI specifications and do not necessarily reflect TI's views; see TI's Terms of Use. TIE2E™OnlineCommunity TI'sEngineer-to-Engineer(E2E)Community.Createdtofostercollaboration amongengineers.Ate2e.ti.com,youcanaskquestions,shareknowledge,exploreideasandhelp solveproblemswithfellowengineers. DesignSupport TI'sDesignSupport QuicklyfindhelpfulE2Eforumsalongwithdesignsupporttoolsand contactinformationfortechnicalsupport. 11.5 Trademarks E2EisatrademarkofTexasInstruments. Allothertrademarksarethepropertyoftheirrespectiveowners. 11.6 Electrostatic Discharge Caution This integrated circuit can be damaged by ESD. Texas Instruments recommends that all integrated circuits be handled with appropriateprecautions.Failuretoobserveproperhandlingandinstallationprocedurescancausedamage. ESDdamagecanrangefromsubtleperformancedegradationtocompletedevicefailure.Precisionintegratedcircuitsmaybemore susceptibletodamagebecauseverysmallparametricchangescouldcausethedevicenottomeetitspublishedspecifications. 11.7 Glossary SLYZ022—TIGlossary. Thisglossarylistsandexplainsterms,acronyms,anddefinitions. Copyright©1999–2017,TexasInstrumentsIncorporated SubmitDocumentationFeedback 19 ProductFolderLinks:INA138 INA168
INA138,INA168 SBOS122E–DECEMBER1999–REVISEDDECEMBER2017 www.ti.com 12 Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information The following pages include mechanical, packaging, and orderable information. This information is the most current data available for the designated devices. This data is subject to change without notice and revision of thisdocument.Forbrowser-basedversionsofthisdatasheet,refertotheleft-handnavigation. 20 SubmitDocumentationFeedback Copyright©1999–2017,TexasInstrumentsIncorporated ProductFolderLinks:INA138 INA168
PACKAGE OPTION ADDENDUM www.ti.com 6-Feb-2020 PACKAGING INFORMATION Orderable Device Status Package Type Package Pins Package Eco Plan Lead/Ball Finish MSL Peak Temp Op Temp (°C) Device Marking Samples (1) Drawing Qty (2) (6) (3) (4/5) INA138NA/250 ACTIVE SOT-23 DBV 5 250 Green (RoHS NIPDAU Level-2-260C-1 YEAR -40 to 125 B38 & no Sb/Br) INA138NA/3KG4 ACTIVE SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 Green (RoHS NIPDAU Level-2-260C-1 YEAR -40 to 125 B38 & no Sb/Br) INA168NA/250 ACTIVE SOT-23 DBV 5 250 Green (RoHS NIPDAU Level-2-260C-1 YEAR A68 & no Sb/Br) INA168NA/3K ACTIVE SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 Green (RoHS NIPDAU Level-2-260C-1 YEAR -40 to 125 A68 & no Sb/Br) (1) The marketing status values are defined as follows: ACTIVE: Product device recommended for new designs. LIFEBUY: TI has announced that the device will be discontinued, and a lifetime-buy period is in effect. NRND: Not recommended for new designs. Device is in production to support existing customers, but TI does not recommend using this part in a new design. PREVIEW: Device has been announced but is not in production. Samples may or may not be available. OBSOLETE: TI has discontinued the production of the device. (2) RoHS: TI defines "RoHS" to mean semiconductor products that are compliant with the current EU RoHS requirements for all 10 RoHS substances, including the requirement that RoHS substance do not exceed 0.1% by weight in homogeneous materials. Where designed to be soldered at high temperatures, "RoHS" products are suitable for use in specified lead-free processes. TI may reference these types of products as "Pb-Free". RoHS Exempt: TI defines "RoHS Exempt" to mean products that contain lead but are compliant with EU RoHS pursuant to a specific EU RoHS exemption. Green: TI defines "Green" to mean the content of Chlorine (Cl) and Bromine (Br) based flame retardants meet JS709B low halogen requirements of <=1000ppm threshold. Antimony trioxide based flame retardants must also meet the <=1000ppm threshold requirement. (3) MSL, Peak Temp. - The Moisture Sensitivity Level rating according to the JEDEC industry standard classifications, and peak solder temperature. (4) There may be additional marking, which relates to the logo, the lot trace code information, or the environmental category on the device. (5) Multiple Device Markings will be inside parentheses. Only one Device Marking contained in parentheses and separated by a "~" will appear on a device. If a line is indented then it is a continuation of the previous line and the two combined represent the entire Device Marking for that device. (6) Lead/Ball Finish - Orderable Devices may have multiple material finish options. Finish options are separated by a vertical ruled line. Lead/Ball Finish values may wrap to two lines if the finish value exceeds the maximum column width. Important Information and Disclaimer:The information provided on this page represents TI's knowledge and belief as of the date that it is provided. TI bases its knowledge and belief on information provided by third parties, and makes no representation or warranty as to the accuracy of such information. Efforts are underway to better integrate information from third parties. TI has taken and Addendum-Page 1
PACKAGE OPTION ADDENDUM www.ti.com 6-Feb-2020 continues to take reasonable steps to provide representative and accurate information but may not have conducted destructive testing or chemical analysis on incoming materials and chemicals. TI and TI suppliers consider certain information to be proprietary, and thus CAS numbers and other limited information may not be available for release. In no event shall TI's liability arising out of such information exceed the total purchase price of the TI part(s) at issue in this document sold by TI to Customer on an annual basis. OTHER QUALIFIED VERSIONS OF INA138, INA168 : •Automotive: INA138-Q1, INA168-Q1 NOTE: Qualified Version Definitions: •Automotive - Q100 devices qualified for high-reliability automotive applications targeting zero defects Addendum-Page 2
PACKAGE MATERIALS INFORMATION www.ti.com 27-Aug-2017 TAPE AND REEL INFORMATION *Alldimensionsarenominal Device Package Package Pins SPQ Reel Reel A0 B0 K0 P1 W Pin1 Type Drawing Diameter Width (mm) (mm) (mm) (mm) (mm) Quadrant (mm) W1(mm) INA138NA/250 SOT-23 DBV 5 250 178.0 9.0 3.3 3.2 1.4 4.0 8.0 Q3 INA168NA/250 SOT-23 DBV 5 250 178.0 9.0 3.23 3.17 1.37 4.0 8.0 Q3 INA168NA/3K SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 178.0 9.0 3.23 3.17 1.37 4.0 8.0 Q3 PackMaterials-Page1
PACKAGE MATERIALS INFORMATION www.ti.com 27-Aug-2017 *Alldimensionsarenominal Device PackageType PackageDrawing Pins SPQ Length(mm) Width(mm) Height(mm) INA138NA/250 SOT-23 DBV 5 250 180.0 180.0 18.0 INA168NA/250 SOT-23 DBV 5 250 180.0 180.0 18.0 INA168NA/3K SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 180.0 180.0 18.0 PackMaterials-Page2
PACKAGE OUTLINE DBV0005A SOT-23 - 1.45 mm max height SCALE 4.000 SMALL OUTLINE TRANSISTOR C 3.0 2.6 0.1 C 1.75 1.45 1.45 B A 0.90 PIN 1 INDEX AREA 1 5 2X 0.95 3.05 2.75 1.9 1.9 2 4 3 0.5 5X 0.3 0.15 0.2 C A B (1.1) TYP 0.00 0.25 GAGE PLANE 0.22 TYP 0.08 8 TYP 0.6 0 0.3 TYP SEATING PLANE 4214839/E 09/2019 NOTES: 1. All linear dimensions are in millimeters. Any dimensions in parenthesis are for reference only. Dimensioning and tolerancing per ASME Y14.5M. 2. This drawing is subject to change without notice. 3. Refernce JEDEC MO-178. 4. Body dimensions do not include mold flash, protrusions, or gate burrs. Mold flash, protrusions, or gate burrs shall not exceed 0.15 mm per side. www.ti.com
EXAMPLE BOARD LAYOUT DBV0005A SOT-23 - 1.45 mm max height SMALL OUTLINE TRANSISTOR PKG 5X (1.1) 1 5 5X (0.6) SYMM (1.9) 2 2X (0.95) 3 4 (R0.05) TYP (2.6) LAND PATTERN EXAMPLE EXPOSED METAL SHOWN SCALE:15X SOLDER MASK SOLDER MASK METAL UNDER METAL OPENING OPENING SOLDER MASK EXPOSED METAL EXPOSED METAL 0.07 MAX 0.07 MIN ARROUND ARROUND NON SOLDER MASK SOLDER MASK DEFINED DEFINED (PREFERRED) SOLDER MASK DETAILS 4214839/E 09/2019 NOTES: (continued) 5. Publication IPC-7351 may have alternate designs. 6. Solder mask tolerances between and around signal pads can vary based on board fabrication site. www.ti.com
EXAMPLE STENCIL DESIGN DBV0005A SOT-23 - 1.45 mm max height SMALL OUTLINE TRANSISTOR PKG 5X (1.1) 1 5 5X (0.6) SYMM 2 (1.9) 2X(0.95) 3 4 (R0.05) TYP (2.6) SOLDER PASTE EXAMPLE BASED ON 0.125 mm THICK STENCIL SCALE:15X 4214839/E 09/2019 NOTES: (continued) 7. Laser cutting apertures with trapezoidal walls and rounded corners may offer better paste release. IPC-7525 may have alternate design recommendations. 8. Board assembly site may have different recommendations for stencil design. www.ti.com
IMPORTANTNOTICEANDDISCLAIMER TI PROVIDES TECHNICAL AND RELIABILITY DATA (INCLUDING DATASHEETS), DESIGN RESOURCES (INCLUDING REFERENCE DESIGNS), APPLICATION OR OTHER DESIGN ADVICE, WEB TOOLS, SAFETY INFORMATION, AND OTHER RESOURCES “AS IS” AND WITH ALL FAULTS, AND DISCLAIMS ALL WARRANTIES, EXPRESS AND IMPLIED, INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION ANY IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE OR NON-INFRINGEMENT OF THIRD PARTY INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHTS. These resources are intended for skilled developers designing with TI products. You are solely responsible for (1) selecting the appropriate TI products for your application, (2) designing, validating and testing your application, and (3) ensuring your application meets applicable standards, and any other safety, security, or other requirements. These resources are subject to change without notice. TI grants you permission to use these resources only for development of an application that uses the TI products described in the resource. Other reproduction and display of these resources is prohibited. No license is granted to any other TI intellectual property right or to any third party intellectual property right. TI disclaims responsibility for, and you will fully indemnify TI and its representatives against, any claims, damages, costs, losses, and liabilities arising out of your use of these resources. TI’s products are provided subject to TI’s Terms of Sale (www.ti.com/legal/termsofsale.html) or other applicable terms available either on ti.com or provided in conjunction with such TI products. TI’s provision of these resources does not expand or otherwise alter TI’s applicable warranties or warranty disclaimers for TI products. Mailing Address: Texas Instruments, Post Office Box 655303, Dallas, Texas 75265 Copyright © 2020, Texas Instruments Incorporated

 Datasheet下载
Datasheet下载